LCD Display Technologies: Reflective, Transmissive, and Transflective
2025-04-01
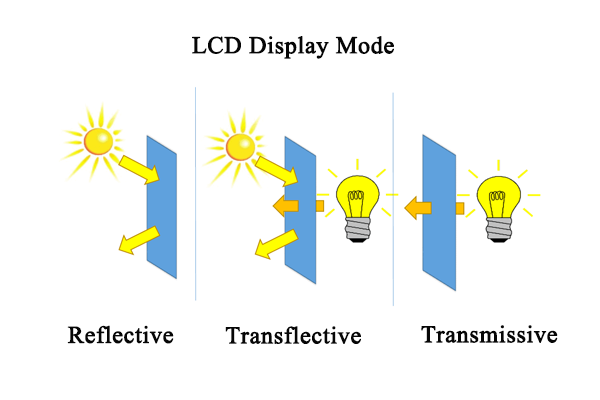
When we talk LCD display modes, we typically classify LCD display modes into three types, mainly including transmissive, transflective, and reflective.
1.Reflective LCD Mode
In reflection mode, ambient light is used to illuminate the display. There is no backlight source inside this kind of display. This is achieved by combining the reflector with the rear polarizer. Reflective LCDs rely on ambient light (e.g., sunlight or indoor lighting) as their primary light source. A reflective layer (often made of metal or highly reflective materials) at the back of the screen redirects incoming light toward the viewer. These displays lack a backlight module, resulting in a simpler design. But there some key features of reflective LCD display mode as below:
- Reflective layer replaces the backlight
- Ultra-low power consumption due to no backlight requirement.
- Lightweight and slim structure.
2.Transmissive LCD Mode
Transmissive LCDs use an integrated backlight as their light source. Light passes through the liquid crystal layer to create images. These screens excel in low-light conditions but may suffer from glare in bright environments. For this kind of display module, light emitting from the back of the display glass must pass by the LCD towards the front to light the pixels. For the transmissive display, the most common devices not only using transmissive LCDs are smartphones, tablets, computer monitors, and television. They are also used in digital cameras, automotive displays, medical equipment, and on on.
Key Feature of Transmissive Mode
- Backlight module positioned behind the LCD panel.
- Liquid crystal layer controls light transmission to produce images.
- Wide Viewing Angles: Technologies like IPS enable clear visibility from multiple angles.
3. Transflective LCD Mode
Transflective LCD mode combine reflective and transmissive technologies. The transflective display mode combine backlight and ambient light to illuminate the pixels. They are combined with backlight and can be used for all types of lighting conditions. They feature both a reflective layer and a backlight. In bright conditions, ambient light is reflected for visibility; in low light, the backlight activates. Therefore, there are some advantage as below:
- Hybrid design integrating a reflective layer and backlight.
- Liquid crystal layer optimized for dual light paths (reflection and transmission).
- Adaptability to All Lighting Conditions: Seamlessly switches between reflective mode (sunlight) and transmissive mode (darkness).
- Balanced Power Efficiency: Reduced reliance on the backlight extends battery life.
- High Contrast and Readability: Enhanced optical design improves visibility in diverse environments.
- Versatility: Suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications.
Summary
|
Type |
Light Source |
Power Use |
Optimal Environment |
|
Reflective |
Ambient light |
Ulta-low |
Outdoor readability |
|
Transmissive |
Backlight |
High |
Low-light/indoor |
|
Transflective |
Ambient and backlight |
Moderate |
Mixed lighting |
Selection Guidelines
Reflective LCD Mode: Choose for ultra-low power needs and outdoor readability (e.g., solar-powered devices).
Transmissive LCD Mode: Prioritize for high-color-accuracy indoor applications (e.g., entertainment systems).
Transflective LCD Mode: Opt for versatile use cases with variable lighting (e.g., sports watches, automotive displays).




