What is COG and COB of LCD Display?
2025-02-20
COG (Chip on Glass) and COB (Chip on Board) are two common packaging technologies in LCD liquid crystal displays, which are used to integrate driver chips into LCD display modules. And it provides various solution scheme for different application scenarios.
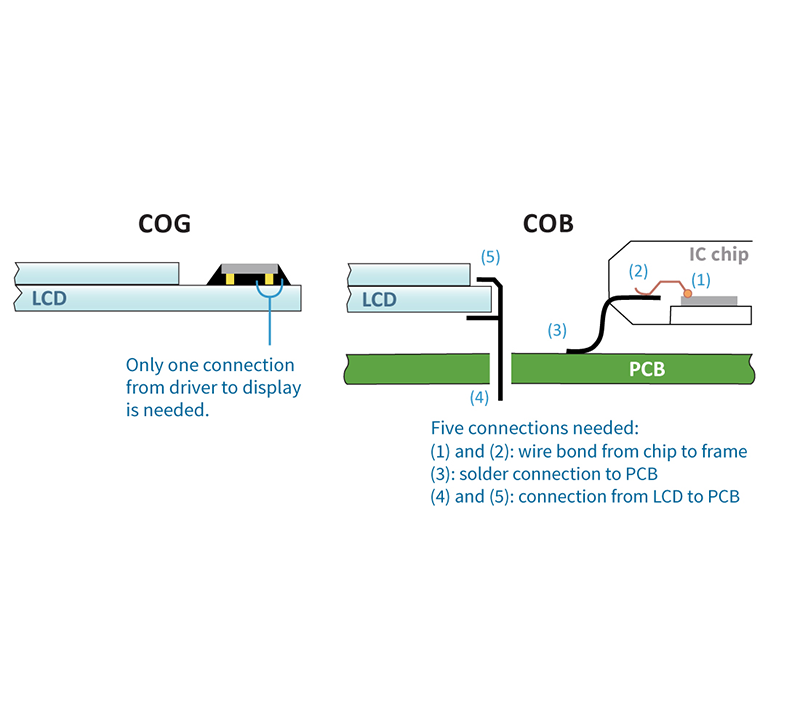
Chip on Glass: COG technology directly bonds the driver IC to the glass substrate.
This technology not only reduces the need for external cable but also significantly enhances the LCD display’s integration level. The standout advantages of COG include its slim design and high reliability, making it an ideal choice for products with stringent requirements on size and weight, such as smartphones and wearable devices.
Chip on Board: COB technology installs the driver IC on the PCB board and then connects it to the LCD module.
The COB process is widely favored for its mature technology and cost-effectiveness. LCD display COB provides greater design flexibility, making it suitable for a variety of complex applications, particularly in industrial equipment, automotive displays, and home appliances. The COB process uses small bare chips with high equipment accuracy, which are used to process PCB boards with a large number of lines, small gaps, and small area requirements. After the chips are soldered and pressed, they are sealed with black glue to prevent external damage to the solder joints and wires, resulting in high reliability.
In summary, COG and COB of LCD display each have their own advantages, and the choice depends on the specific application requirements. COG is suitable for high integration and thin design, while COB is suitable for cost-sensitive and flexible design scenarios.